Curious about plant protein, how to use it, what are the best plant-based protein foods, and why you should be eating plant protein foods?
So are a ton of other people!
Our core food philosophy is to eat a plant-centric diet, which to us, means focusing on whole foods and mostly (you guessed it!) plants!
Regardless of what lifestyle you practice — whether you’re simply looking to add more plant-based foods into your diet or if you’re transitioning to a fully plant-based diet and lifestyle — we all can benefit from a diet rich in plants, along with the fiber, minerals, phytonutrients, and health benefits that they provide.
But, I get asked all the time, “How can I get enough protein without eating meat?”
There are ample plant-based foods where you can get plant-based protein — it’s just a matter of learning what they are, how to use them, and being mindful to incorporate them into tasty and easy meals each day.
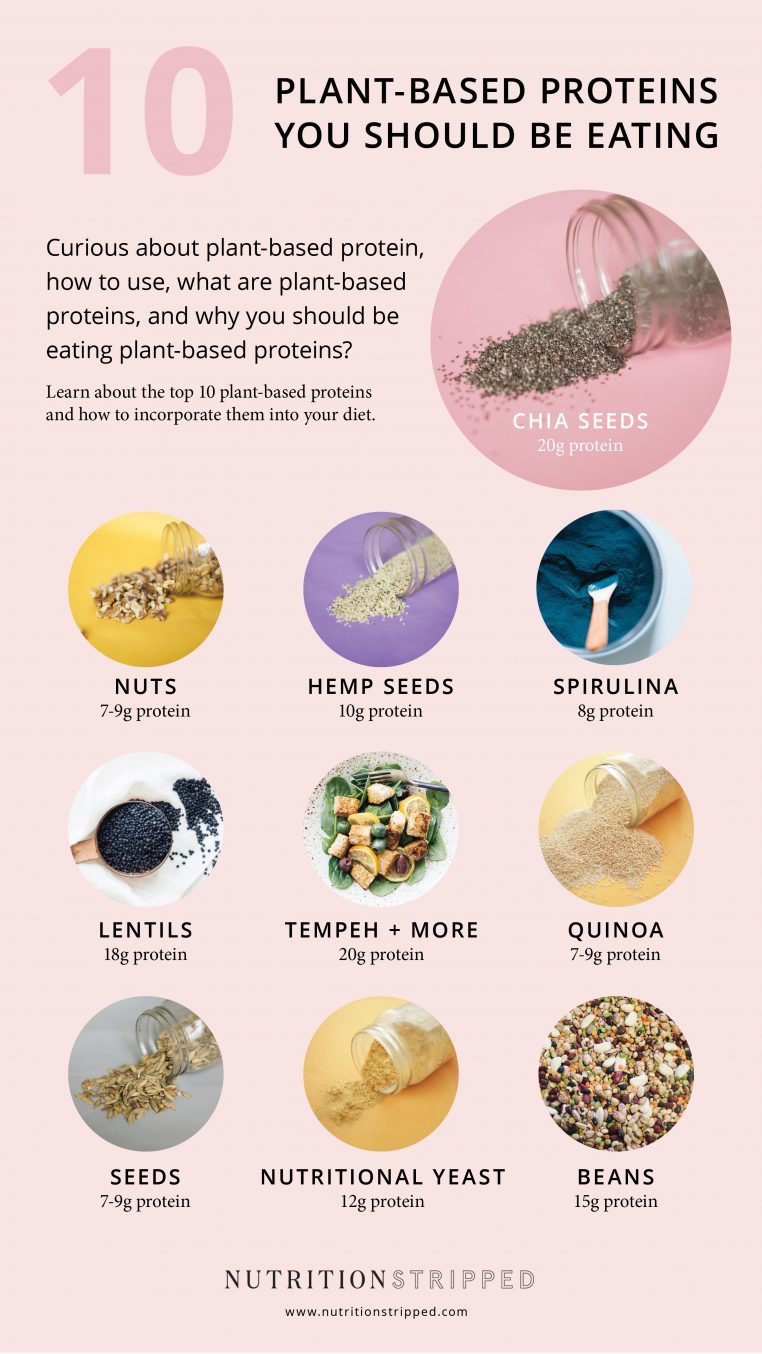
Top 10 Sources of Plant-Based Protein
1. Plant Protein: Lentils
Lentils are a great source of carbohydrates and fiber as well as protein. In fact, they offer over 10 grams of muscle-building protein in a single serving. Lentils are considered to be a starchy protein, and split green peas can be also added to the same category as lentils.
Lentils contain a mix of both essential and non-essential amino acids, including globulin, which makes up almost half of the lentils’ amino acid profile. Besides these amino acids, lentils promote health through their content of starch, insoluble dietary fiber, prebiotics, and potassium (1). To top it off, lentils are very inexpensive, easy to prepare, and super filling.
Lentils Nutrition:
- 1/2 cup cooked lentils = 12 grams of protein
- 1/2 cup of green peas = 4 grams of protein
How to Use Lentils:
- Cook with your favorite spices and seasonings and enjoy plain
- Top on salads, Lentil Nourish Bowls, or One Bowl Skillet Meals
- Try them in the Simple Plant-Based Lentil Bolognese or Simple French-Inspired Lentil Salad
- Whip up Lentil Sloppy Joes or Red Lentil Daal with Squash and Coconut
- Combine with rice or quinoa for a hearty meal
- Use to make vegetarian meatballs, loaves, or burgers
- Use as a taco filling or meat sauce for spaghetti
- For more information on the nutrition and health benefits of lentils, click here
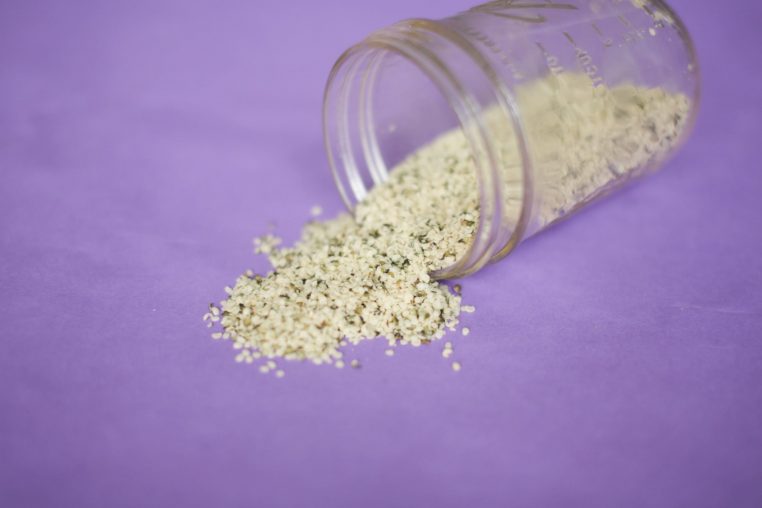
2. Plant Protein: Hemp Seeds
Hemp seeds not only contain protein but also supply plenty of heart-healthy fats, mainly omega-3 fatty acids. Though they don’t contain all amino acids (they’re missing lysine), they are still considered an excellent source of protein for vegans. It’s interesting to note, too, that hempseed oil contains all the essential amino acids, along with one called arginine, which helps with the production of nitric oxide, a vital molecule for a strong cardiovascular system (2).
Hemp seeds have a delicious, subtly sweet and nutty flavor and are so small in size that they can easily be used and added to any recipe to boost the plant protein content.
Hemp Seeds Nutrition:
- 3 tablespoons hemp = about 10 grams of protein
How to Use Hemp Seeds:
- Sprinkle on top of salads (like the Kale Hemp Tabbouleh)
- Stir or blend into soups or stews to slightly thicken
- Add to smoothies for a creamy texture
- Make Hemp Seed Milk
- Whip up Crunchy Chocolate Seed Bark or Hemp Seed Crumble
- Blend into hummus, dips, or dressings
- Sprinkle on top of porridge, oatmeals, or other cereals
- Add into baked goods and desserts for added protein
- For more information on the nutrition and health benefits of hemp seeds, click here
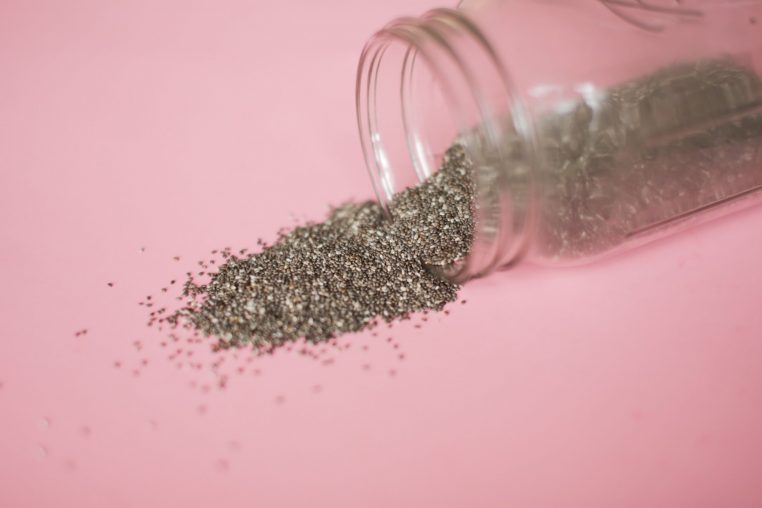
3. Plant Protein: Chia Seeds
Chia seeds are ancient seeds that have been used for centuries for their amazing ability to absorb water and turn into a gel-like substance, which is thanks to the soluble fiber content in the seeds. Because of this unique characteristic, chia seeds are great to add to meals and foods to help thicken them naturally while also boosting the content of fiber, protein, and healthy fats (mainly omega-3’s).
As for protein, in particular, chia seeds are made up of about 20% protein and 25% fiber. While the protein level can vary from batch to batch of these seeds depending on where they’re grown, they do contain both essential and non-essential amino acids, with most of them being globulin (3). Chia seeds are also a naturally gluten-free protein, which is helpful for those with sensitivities.
Chia Seed Nutrition:
2 tablespoons = 4 grams of protein
How to Use Chia Seeds:
- Sprinkle on top of porridges, oatmeal, and cold cereals for an added crunch
- Soak for at least 30 minutes in almond milk to make a basic chia seed pudding
- Add to water for a refreshing and hydrating Chia Fresca/Bubble Water
- For more information on the nutrition and health benefits of chia seeds, click here
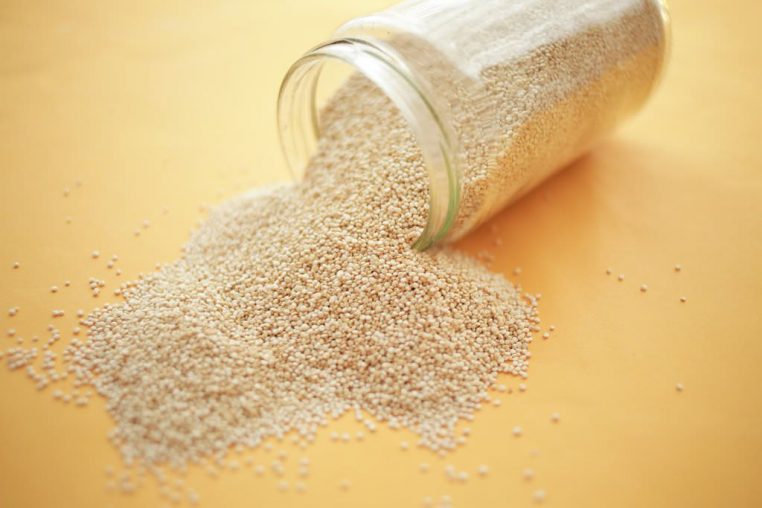
4. Plant Protein: Quinoa
Quinoa is a gluten-free grain (technically a seed) that is used as a carbohydrate and considered one of the top plant-based protein foods. It’s often classified as a starchy protein because it contains carbohydrates, as well as ample amounts of plant protein and fiber. Use it in place of rice for more diversity in your carbohydrate intake, and a little added protein with those carbs.
Compared to other grains, quinoa has a better amino acid profile and higher protein to fat and carb ratio (4). It’s also higher in the amino acid lysine compared to wheat, corn, or rice.
Quinoa Nutrition:
1/2 cup cooked quinoa = 7-9 grams of protein
How To Use Quinoa:
- Cook and use to top off raw or cooked greens
- Add to a Nourish Bowl, Beauty Bowl with Turmeric Eggs, or One Bowl Skillet Meal
- Use as a hot or cold cereal by adding homemade nut milk and fresh fruit
- Enjoy a bed of quinoa instead of a bed of rice for stir-fry dishes or as a side dish
- Try quinoa with other plants high in protein in Black Bean and Quinoa Taco Lettuce Wraps
- Add quinoa to salads like the Warm Quinoa Salad, Curry Quinoa Salad, Loaded Quinoa Salad, and Apricot Quinoa Summer Salad
- Stuff quinoa in a veggie like the Moroccan Stuff Quinoa Peppers
- Quinoa can also be used as a pilaf, such as the Citrus Quinoa Pilaf and Cheezy Quinoa Broccoli Pilaf
- For more information on the nutrition and health benefits of chia seeds, click here
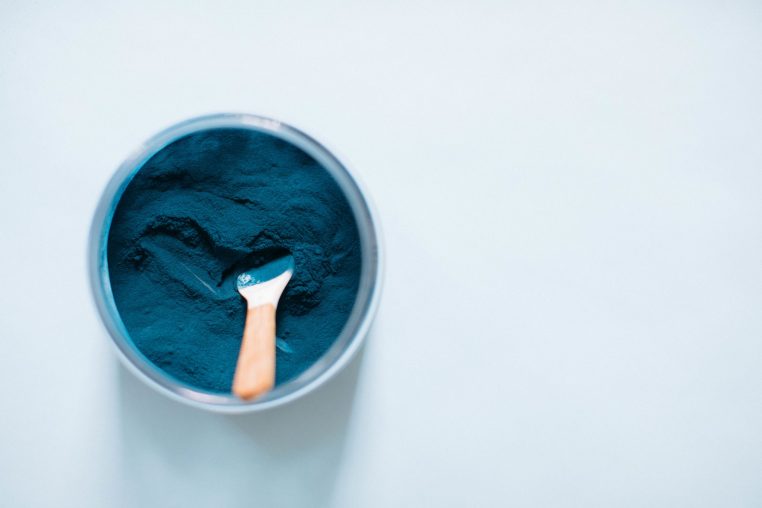
5. Plant Protein: Spirulina
Spirulina is incredibly protein-rich and one of the few sources of high-protein plant foods that is mostly made of the macronutrient by dry weight. In fact, spirulina is comprised of about 6o% to 70% protein by weight, whereas most other plant proteins are made up of only about 35% (5). Plus, spirulina provides all essential amino acids, making it a complete protein. Research also shows that your body can use the protein from spirulina more efficiently, making it one of the best plant protein sources available (5).
It’s deep blue-green in color and will change anything you mix with it into that vibrant color. It tastes subtly sweet and nutty, with hints of vanilla and chocolate, but with a subtle seaweed flavor.
Spirulina Nutrition:
- 2 tablespoons spirulina = 8 grams of protein
How to Use Spirulina:
- Blend into smoothies, such as the Tropical Green Smoothie, Seabreeze Spirulina Smoothie, or Beauty Green Smoothie
- Use in snack or dessert recipes, such as the Spirulina Energy Globes or Mint Chocolate Feel Amazing Fudge
- Sprinkle spirulina on the Mint Mocha Steamer for an added boost of vegan protein
- For more information on the nutrition and health benefits of spirulina, click here
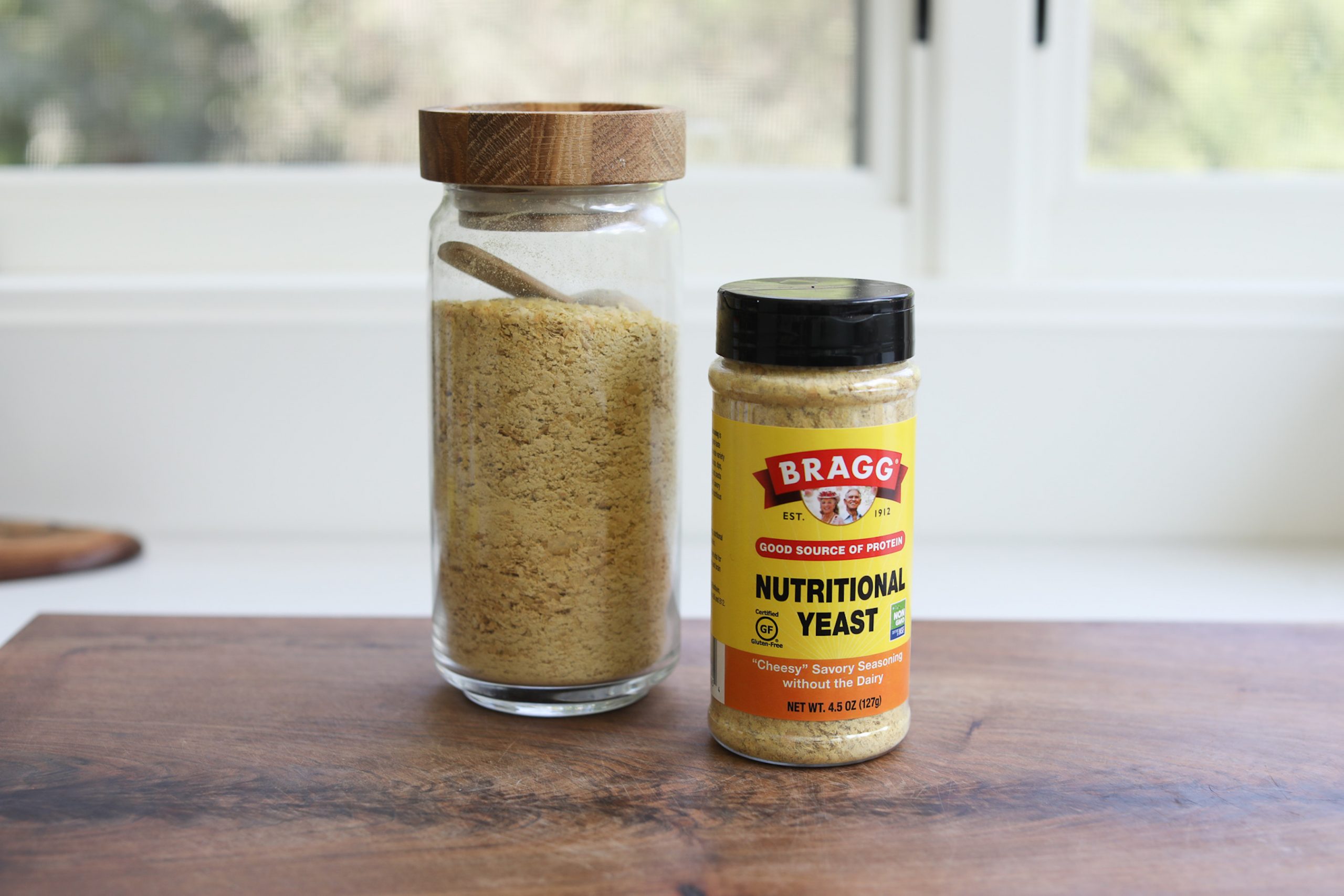
6. Plant Protein: Nutritional Yeast
Nutritional yeast by Bragg is one of the top high-protein plant-based foods thanks to its cheesy flavor, versatility, and impressive nutrient content. Nutritional yeast contains no dairy or active yeast, and it’s found in a powder/flake form that creates a paste when mixed with liquid. It’s great for making dairy-free sauces, dressings, and more.
Another complete protein, you’ll get all amino acids in a serving of nutritional yeast. It’s an easy way to bump up the macronutrient in your meals when you just sprinkle it on top of a dish, just as you would regular cheese.
Nutritional Yeast Nutrition:
3 tablespoons nutritional yeast = about 12 grams of protein
How to Use Nutritional Yeast:
- Add flaked nutritional yeast to almond milk or water to create a cheesy dressing or sauce
- Sprinkle on top of salads, quinoa, lentils, beans, and more for a cheesy flavor
- Incorporate into dips such as hummus, Baba Ghanoush or Classic Cashew Cheese
- Use it for a cheesy flavor in Cauliflower Alfredo Sauce
- Sprinkle it on popcorn for an added flavor boost
- Try it in homemade Cauliflower Pizza Crust
- For more information on the nutrition and health benefits of nutritional yeast, click here
- For recipes using nutritional yeast, click here
7. Plant Protein: Seeds
Seeds such as sunflower, sesame, chia, hemp, flax, and pumpkin seeds are all rich in both protein and minerals, earning them a slot on the list of best vegan protein foods. Seeds vary by type, and some are nuttier in flavor whereas others are more sweet and neutral tasting. Pumpkin seeds have an earthy flavor, sesame seeds are very nutty-tasting, sunflower seeds are slightly sweet and nutty, and flax and chia seeds taste mildly nutty.
Like most plant proteins, these seeds lack lysine, the amino acid most need to make a complete protein. That doesn’t mean they’re not great sources of the macronutrient, though. For instance, pumpkin seeds are made up of nearly 60% protein (6), so you’ll be getting a good bang for your buck with a 1/4 cup serving.
Seeds Nutrition:
1/4 cup seeds = around 7-9 grams of protein
How To Use Seeds:
- Sprinkle seeds on top of salads or any meal to increase the healthy fat and protein content using this Simple Seed Mix
- Use in granola, Nourishing Muesli, or other baked goods
- Grind and use as a “flour” in gluten-free baking
- Pulse coarsely and use in desserts such as the Raw Peach Tart
- Use in desserts, snacks, truffles, and raw bars for a nutrient-dense boost
- Blend into homemade seed butter
- Sprinkle on top of oatmeal, porridges, or cold cereals for crunch and protein
- For more information on the nutrition and health benefits of seeds, click here
8. Plant Protein: Nuts
Nuts such as almonds, walnuts, cashews, pistachios, Brazil nuts, and more are not only rich in minerals, vitamin E, and healthy fats but they’re also high in protein. Nuts vary by type, and some are nuttier in flavor whereas others are more sweet and neutral tasting. Cashews are one of my favorite nuts as they’re incredibly versatile to use in sweet and savory dishes. Brazil nuts are my close second favorite because they’re rich in selenium. In fact, eating just one serving a day makes up 100% of your DV for selenium.
People often add nuts to meals or as snacks for the strong mix of protein and fat—two nutrients that help to fill you up and keep you full. While nuts do provide a great source of plant protein, they don’t contain all the full line-up of amino acids. Most lack lysine, while others (like almonds) don’t have sulfur amino acids, methionine and cysteine, or tryptophan (namely, macadamia and pecans), and threonine (an amino acid that peanut is missing) (7).
Nuts Nutrition:
1/4 cup nuts = around 7-9 grams of protein
How to Use Nuts:
- Sprinkle nuts on top of salads or any meal to increase the healthy fat and protein content
- Use in granola, Nourishing Muesli, or other baked goods
- Grind and use as a “flour” in gluten-free baking
- Add them to a dessert like Pistachio Ice Cream
- Grind or pulse coarsely and use in desserts such as the Raw Peach Tart
- Use in desserts, snacks, truffles, and raw bars for a nutritious boost
- Blend into your own nut butter
- Sprinkle on top of oatmeal, porridges, or cold cereals for added crunch and protein
- For more information on the nutrition and health benefits of nuts, click here
9. Plant Protein: Beans
Beans and legumes like chickpeas are an amazing source of plant protein, carbohydrates, and fiber. Beans are considered to be a starchy protein, just like lentils. Magnesium is another key player in beans, which is an important mineral in our body that plays a key role in 300 cellular functions, including muscle function, protein synthesis, blood sugar control, and blood pressure regulation. It’s also been shown to help decrease PMS symptoms, headaches, and constipation.
Beans contain many amino acids such as isoleucine, but they still lack others like valine and lysine. One study also found that you’ll digest anywhere from 33% to 86% of the amino acids available in beans, a percentage that varies across types of beans, including black, red, and white (8).
Beans Nutrition:
- 1 cup cooked beans = around 15 grams of protein
How to Use Beans:
- Cooked with your favorite spices and seasonings and eaten plain
- Top on salads, Nourish Bowls, or One Bowl Skillet Meals
- Combine with rice or quinoa for a hearty meal
- Use to make vegetarian meatballs, loaves, or burgers
- Use as a taco filling or meat sauce for spaghetti
- For more information on the nutrition and health benefits of beans, click here
- For recipes using beans, click here
10. Plant Protein: Organic Tempeh, Tofu, and Edamame
Soy-containing foods such as tempeh, tofu, and edamame all offer a complete plant protein containing all amino acids. They are one of the strongest, most animal-like protein in terms of chemical makeup. Some research also says that soy has a high concentration of BCAAs or branched-chain amino acids, which are beneficial to athletic performance (9).
Oftentimes, these soy-based sources of plant protein also contain fiber and healthy fats in addition to protein. Tempeh is the most nutritious out of this bunch, as it contains naturally-occurring healthy bacteria from the fermentation process. However, be sure to read up about what you should know about soy before adding a ton of tempeh, tofu, or edamame to your diet.
Soy Nutrition:
1 serving of tempeh/tofu/edamame = around 20 grams of protein
How to Use Tempeh, Tofu, and Edamame:
- Use as you would beans or lentils
- Swap in as a simple meat substitute since tofu and tempeh both can be marinated. Try a Buffalo Tempeh Nourish Bowl, Baked Citrus Tempeh, The Best Cooked Tofu, The Easiest Tofu Tikka Masala, or Bahn Mi Tofu Tacos!
- Use tempeh and tofu as toppings to salads like the Simple Kale Caesar Salad
- Add to stir-fry meals like the Peanut Tempeh Stir Fry
- Mix into plant-based sauces, such as “meat” spaghetti sauce
- Use as filling for tacos, burgers, or even shaped into “hot dogs”
- Shopping tip: always purchase organic and sprouted tofu if available, non-GMO if available
Living a plant-based lifestyle, as we often recommend at Nutrition Stripped, is all about choosing fruits, veggies, whole grains, and the above-mentioned plant-based protein sources. Finding the foods that make you feel best and keep you full, energized, and satisfied is the key to following a healthy eating plan and still enjoying the foods you love.
BECOME A LIFELONG BALANCED EATER
In order to make your nutrition and lifestyle habits stick, a combination of these strategies needs to be utilized.
This is exactly what we kept in mind when we built the Mindful Nutrition Method.
The Mindful Nutrition Method™ is a transformative online live experience with live group coaching, training and course materials, and a private community. Inside we teach our students how to create balanced eating habits for life that help you be free from food and diet obsession, maintain a balanced weight, cultivate a positive relationship with food and your body, and ultimately find joy in nourishing yourself.
Are you feeling stressed about food?
Sign up to watch our free masterclass today, where you’ll learn about #1 Habit That Keeps You Struggling With Your Weight and Relationship With Food — And How To Break Free From The Diet And Food Obsession Starting Now.
You don’t need to stress and obsess about food. There is a better way, and yes it’s possible to cultivate a positive relationship with food! Join this free balanced eating masterclass to learn how.